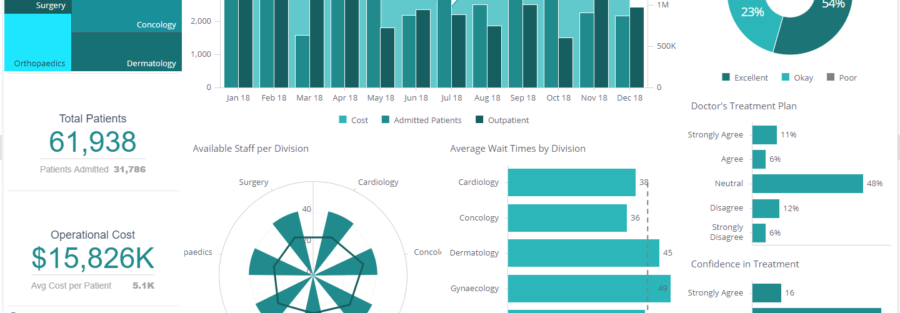
Here is the complete list of the 15 most important healthcare KPIs and metrics that hospital managers and professionals need to know:
- Average Hospital Stay: Evaluate the amount of time your patients are staying
- Bed Occupancy Rate: Monitor the availability of hospital beds
- Medical Equipment Utilization: Track the utilization of your equipment
- Patient Drug Cost Per Stay: Improve cost management of medications
- Treatment Costs: Calculate how much a patient costs to your facility
- Patient Room Turnover Rate: Balance the turnover with speed and quality
- Patient Follow-up Rate: Measure the care for your patients over time
- Hospital Readmission Rates: Track how many patients are coming back
- Patient Wait Time: Monitor waiting times to increase patient satisfaction
- Patient Satisfaction: Analyze patient satisfaction in detail
- Staff-to-Patient Ratio: Ensure you have enough staff to care for your patients
- Canceled/missed appointments: Keep track of patients’ appointments
- Patient Safety: Prevent incidents happening in your facility
- ER Wait Time: Identify rush hours in your emergency room
- Costs by Payer: Understand the type of health insurance of your patients
Average Hospital Stay
Performance Indicators
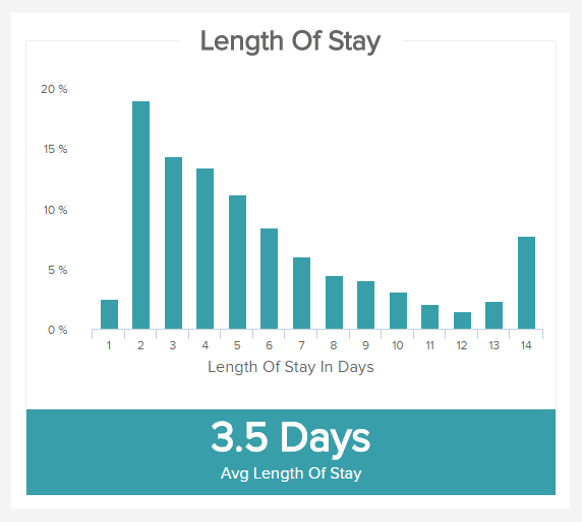
After different evaluations over this KPI, you may set a target length of stay (accordingly to the type of stay and procedure) that you would like to achieve.
Evaluate the amount of time your patients stay
The average length of stay in hospital is a pretty straight-forward KPI, as it measures the time spent, on average, by a patient accepted in the facility. This healthcare metric is a very general one and can vary according to the type of stay it measures: a heart transplant surgery will increase the figure while a wisdom teeth removal will do the opposite. This is why it is interesting to breakdown this KPI in different categories of stay, procedures, and operations, so as to have a more accurate result. You can also measure it depending on the different units of your hospital.
Bed Occupancy Rate
Performance Indicators
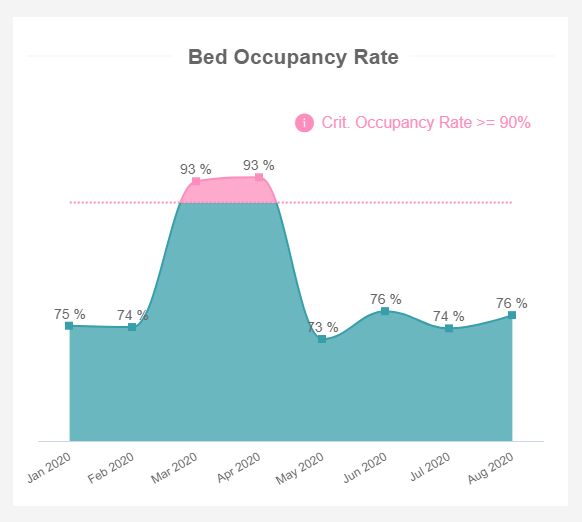
Monitor the occupancy rate in order to establish a healthy balance between the utilization of hospital resources and general pressure on the facility.
Monitor the availability of hospital beds
Our list of key performance indicators in healthcare wouldn’t be complete without the bed occupancy rate. It’s an important element of analytics, and it quickly shows how many beds were occupied during a specific period, expressed in percentage. In the visual example, you can immediately observe 2 critical months, March and April, when the occupancy rate was above the critical threshold of 90%. Luckily, the next month brought positive change and the occupancy went down. Higher occupancies could mean a number of things such as a pandemic but the goal is to keep the occupancy under control, otherwise, there are risks of extreme facility pressure and higher numbers of infection.
Medical Equipment Utilization
Performance Indicators
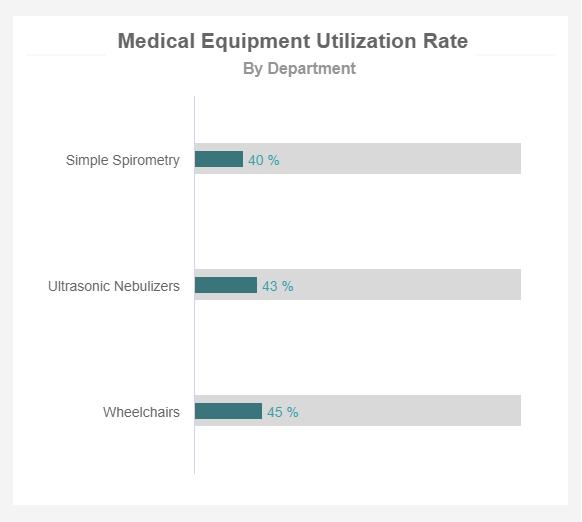
Track the utilization rate to identify where is room for improvement such as reallocation of equipment where is needed the most.
Monitor the availability of hospital beds
Technological advancements and more treatment options for patients mean higher numbers of medical equipment available. This could lead to increased costs of maintenance, wrong purchasing decisions, or lower quality of patient care. That’s why hospital key performance indicators such as the medical equipment utilization rate are critical in establishing better asset management processes. Turning to modern dashboard software that created the example on the left will enable hospital leaders to effectively allocate necessary resources and ensure that the equipment is used for optimal needs. For example, reallocate the spirometer from the area of low utilization rate to the area of higher utilization as the usage fluctuates.
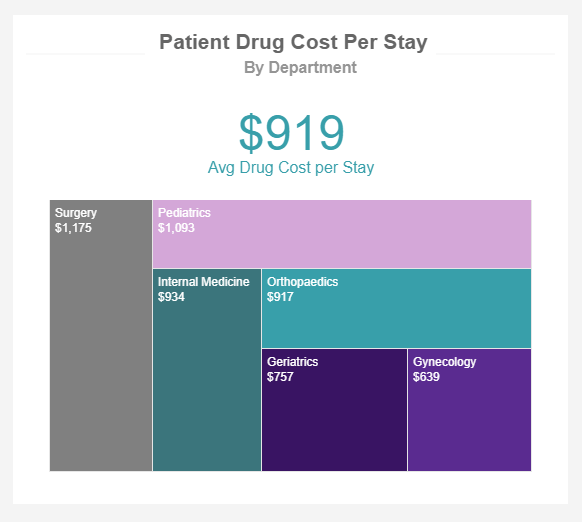
Patient Drug Cost Per Stay
Performance Indicators
Monitor the average drug cost per stay as well on the departmental level in order to effectively allocate monetary resources.
Improve cost management of medications
Access to patients’ drugs as well as costs is one of the major elements in hospital management, but also healthcare systems as a whole. If the hospital is not able to provide relevant medications, patient care will suffer, hospitals will experience budget pressures, and, consequently, a shortage of staff due to budget cuts. That said, this is a medical KPI that needs special attention and continuous monitoring. Our example shows relevant departments and the average cost per stay, where surgery and pediatrics lead with over $1000, and internal medicine and orthopedics follow. These insights can help to evaluate future budget allocations, if the hospital expects higher numbers of surgeries, it makes sense to order relevant medications.
Treatment Costs
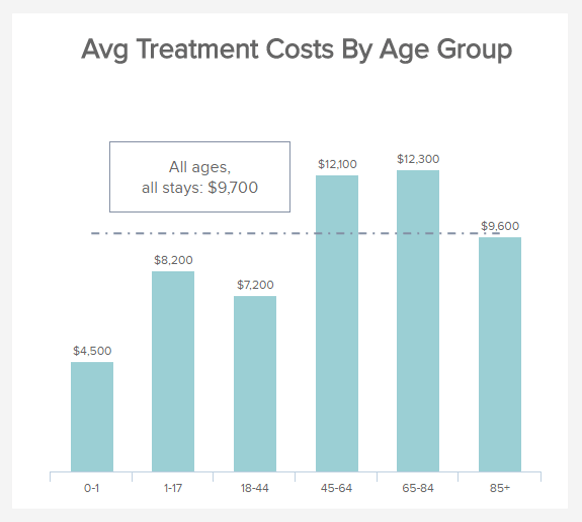
Performance Indicators
Calculate the treatment costs according to different categories over time and analyze the evolution.
Calculate how much a patient costs to your facility
This a typical healthcare KPI example for monetary management. Treatment costs are important metrics to track as they directly impact your finances, the contribution margin you make, and the capacity of your facility to sustain itself. The purpose is not to reduce it as much as possible to make a profit, but to spot abnormal or exaggerated expenses and address them. You can break it down into various categories -per units, per operations, or as in our example, per age groups. By acknowledging these costs, you can also budget better and allow the right amount of money to go to the right category: 25-year-old patients cost on average less than 72-year-old patients.
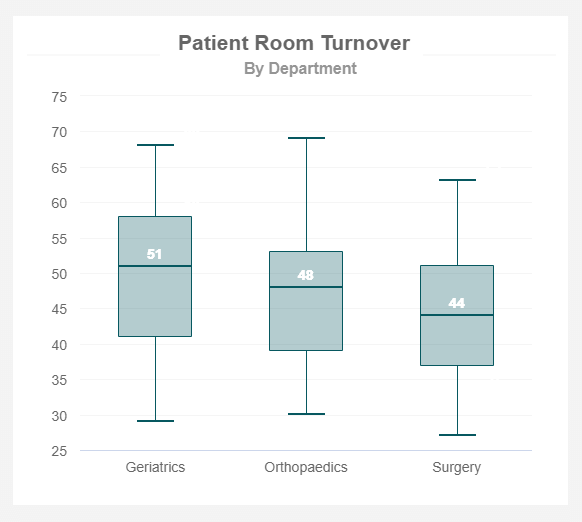
Patient Room Turnover Rate
Performance Indicators
To improve the room turnover rate, include high-quality standards of cleaning services, and introduce a tracking system to know which beds are available.
Balance the turnover with speed and quality
In order to improve the operational performance of your hospital, the room turnover rate is one of the hospital metrics that have to be taken into account. When the patient leaves the room, activities such as cleaning, evaluating the equipment, preparing the room for another patient to enter, and changing medical materials all fall under the turnover. The goal is to create a speedy process but ensure quality. This is important as lower quality can cause higher risks of infections and affect numerous other metrics such as costs. To improve the turnover rate, establish a reliable cleaning service, whether in-house or external, that is also sensitive to patient safety and other hospital regulations.
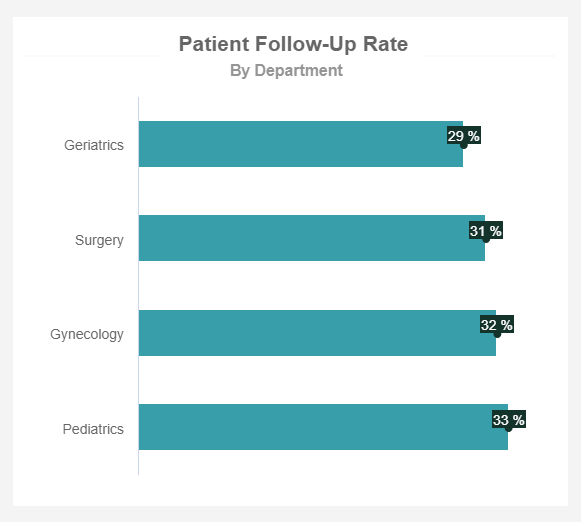
Patient Follow-up Rate
Performance Indicators
To successfully guide patients through their recovery process, monitor the follow-up rates by departments, and see what kind of care patients need the most.
Measure the care for your patients over time
The patient follow-up rate is one of the healthcare performance metrics that deal with patients’ care after finishing a particular treatment. Treatments include simple medical check-ups, physical exams, a new prescription, blood tests, or consultations, among others. The follow-up can be done by a physician, nurse, or administrator, e.g., depending on the type of need. For example, a follow-up on cancer patients has its purpose to see if the disease returned or spread across the body so it might make sense to track this rate by the department to see what kind of needs patients have regarding the type of treatment (surgery, gynecological issues or pediatric follow-ups). That way, the hospital has a better overview of particular departmental performance and, consequently, improves patient outcomes.
Hospital Readmission Rates
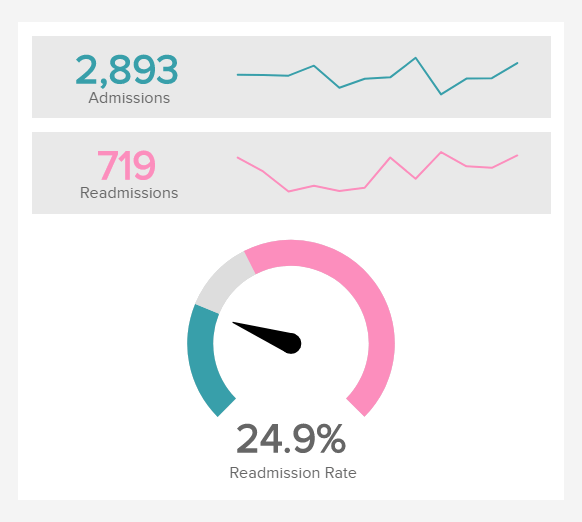
Performance Indicators
The lowest your readmission rate is, the better. High rates point out dysfunctionalities that must be addressed as soon as possible.
Learn how many patients are coming back
A typical healthcare KPI example here. The hospital readmission rate provides information on the number of patients that return to the hospital within a short period of time after being released. It is one of the most important healthcare metrics as it provides great insight into the quality of care administered in the facility concerned — but cannot be used as a stand-alone quality indicator. Readmission rates can also shed the light on other flaws the hospital management is subjected to (lack of staff or appropriate material, overloaded staff neglecting details, units with special need …), and may help in better cost control as it aims to decrease expensive and unnecessary readmissions.
Patient Wait Time
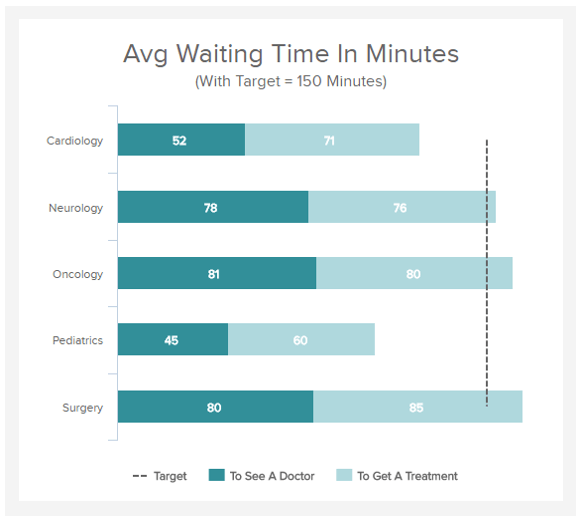
Performance Indicators
The lower the wait time is the better. Measuring this type of healthcare KPI over time is also important so as to identify trends and rush hours on a longer time period, and eventually adjust staffing needs for more efficient patient management.
Decrease patients’ waiting time
Patient wait time is one of the most important aspects of patient contentment. It measures the time it takes for anyone visiting your hospital from when they register to when they see a doctor and get treatment. It can be particularly interesting to measure it in ER (emergency rooms) to evaluate how prompt the hospital to deliver urgent services to its patients is. This healthcare metric is highly linked to the patient satisfaction score, as no one really enjoys staying hours in a hospital. It can also reveal some other problems your facility is facing, if the figure is too high, and that needs to be addressed.
Patient Satisfaction
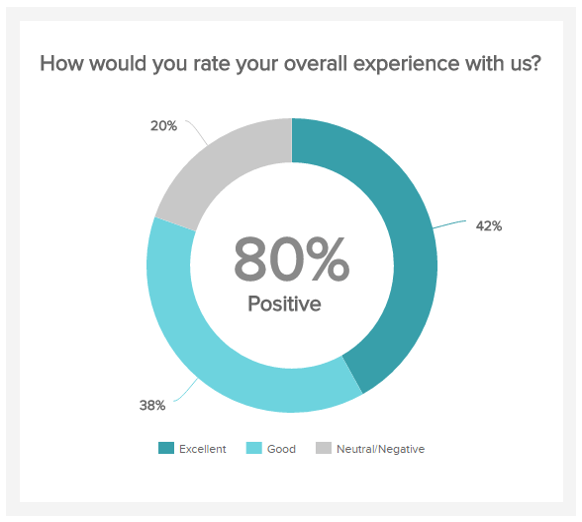
Performance Indicators
The overall patient satisfaction is precisely the healthcare KPI that will attract or on the contrary scare away future patients. The higher it grows, the better it is.
The showcase of your healthcare facility
This is another great healthcare KPI example that should be a top priority for any healthcare organization, in order to have feedback and improve the service. You can ask your patients how they felt while being taken care of, how they would rate their meals, or the time taken by doctors and nurses to explain their situation. Such assessment will provide you insights on the overall perception of your hospital services and show you which points can be improved. Besides, your patients will feel listened to as their opinion and feelings are taken into account, which is another important component of the satisfaction score.
Staff-to-Patient Ratio
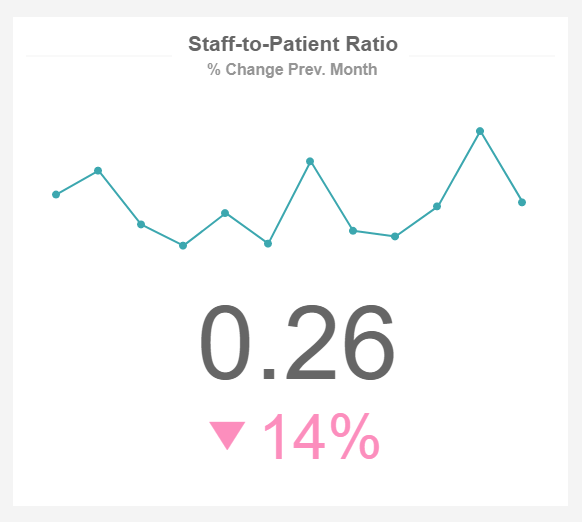
Performance Indicators
Evaluate your staff-to-patient ratio on a regular basis so that you avoid staff fatigue, increase patient satisfaction, and reduce potential errors.
Ensure you have enough staff to care for patients
The staff-to-patient ratio indicates whether your staff management processes are effective, meaning whether the hospital is understaffed or overstaffed. Personnel must be available to provide care to all patients, no matter the time of the day, and immediately, if issues arise. Different states have different regulations, but the goal is to provide optimal treatment and ensure each patient is taken care of when needed. In our example, we can see that a change occurred, in comparison to the previous month, and the staff-to-patient ratio reduced by 14%. Here it would make sense to investigate why and if this drop has caused bottlenecks.
Canceled/ missed appointments
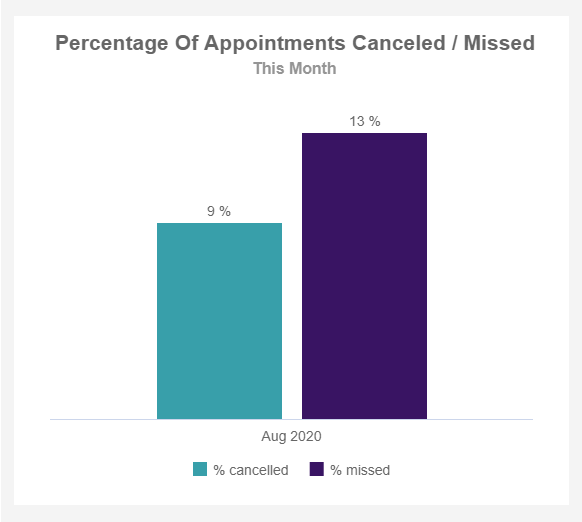
Performance Indicators
Measure this value over time so you can address the issues and improve the attendance via reminders or additional calls to patients, for example.
Keep track of patients’ appointments
This is one of the key performance indicators for outpatient clinics as well as hospitals, important because it directly affects the efficiency of clinicians. If patients don’t attend the scheduled appointment, the result is a waste of resources but also the relationship with the physician suffers since one of the consequences includes a violation of trust. Canceled appointments are also affecting the facility’s performance, but, in this case, if canceled on time, doctors and nurses have the chance to rearrange the schedule and bring another patient in. Forgetfulness, unable to get time off work/school, sickness, transportation issues, and many other factors can influence this metric so you should keep in mind the causes that increase the percentage of canceled or missed appointments.
Patient Safety
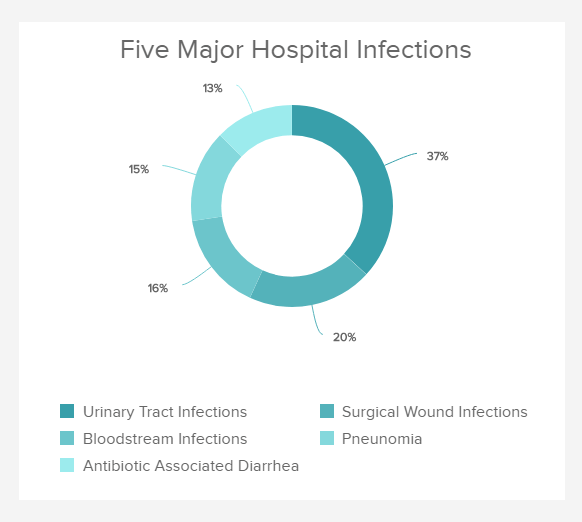
Performance Indicators
This healthcare KPI provides data on the quality of care your hospital delivers to its patients. It will give you insights on what must be improved in the different services.
Identify the incidents happening in your facility
The patient safety measures the capacity of a hospital to deliver quality care to its patients and keeping them safe from contracting a new infection, post-operation complications, or any kind of sepsis. This is extremely important to track this metric assiduously to know where problems occur, which stage of the process can be improved, and identify any infection abnormally present in your hospital. You can measure this metric and break it down into distinct categories (post-operation infections, respiratory infections, or treatment-related diseases), to have an even more accurate view of your hospital performance in the matter.
EMERGENCY ROOM (ER) WAIT TIME
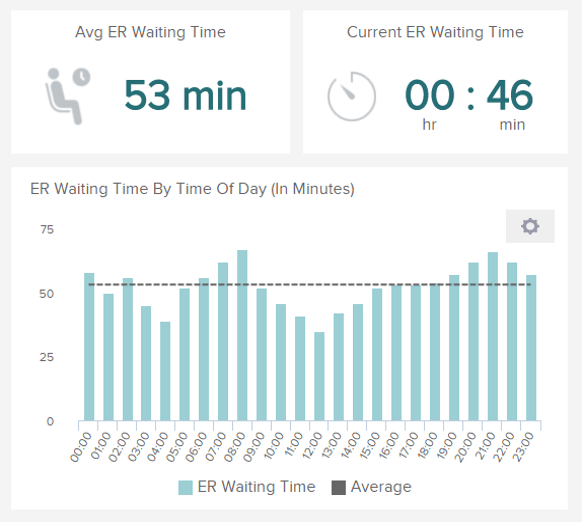
Performance Indicators
After assessment of the ER wait time on average, you should keep an eye on the evolution of that metric and monitor it over time to see trends, so as to adjust or solve any issue popping up.
Evaluate the time patients spend in the ER
ER or emergency room wait time measures the amount of time between the arrival of a patient in the ER and the moment he or she can see a physician. This number is linked to the average patient wait time, but is more specific as it focuses on the emergency room only. Evaluate this KPI so as to know when the rush hours of the day are and the busiest days of the week, how long are your patients currently waiting and set a target accordingly. Just like for the patient wait time, it may spark light on issues (staff overloaded, check-in processes needing change, ER facilities congested) the service is facing and that can become very problematic if not solved.
Costs by Payer
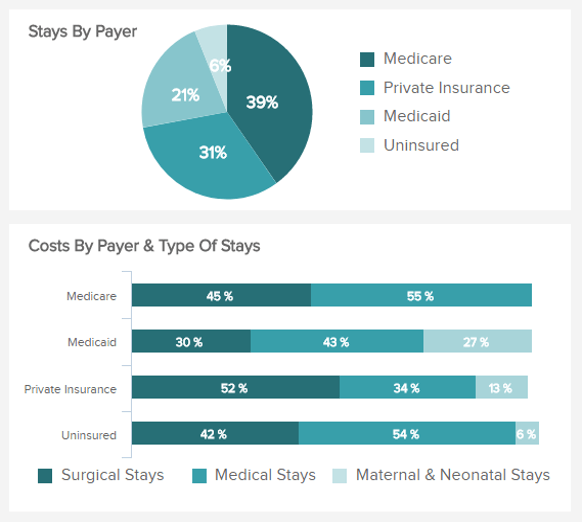
Performance Indicators
A good assessment of the healthcare providers that are covering your patients is important to track your patients’ satisfaction.
Identify the biggest payers for your facility
This healthcare metric will evaluate the distribution of the costs amongst the different organisms. Whether your patients are under Medicare, Medicaid, whether they subscribe to private insurance or do not have any insurance at all, this metric will help you know which organisms are the biggest payers for your health facility. This will also tell you what types of stay and how much they represent for each healthcare provider: surgical, medical, maternal, and neonatal stay. According to the insurance and the type of stay, the average amount of time they take to pay varies, and knowing how much they represent will help you manage better the financial management of your healthcare facility.